What Kind of Oil Does My Car Take?
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Engine Oil for Peak Performance and Longevity
Understanding the Importance of Engine Oil
Engine oil is the lifeblood of your vehicle. It lubricates moving parts, reduces wear and tear, removes contaminants, and ensures your engine runs smoothly. Choosing the right oil for your car isn’t just about topping up when the level is low—it’s about using the correct motor oil grade, understanding oil viscosity, and meeting the OEM oil specifications.
How to Determine What Kind of Oil Your Car Takes
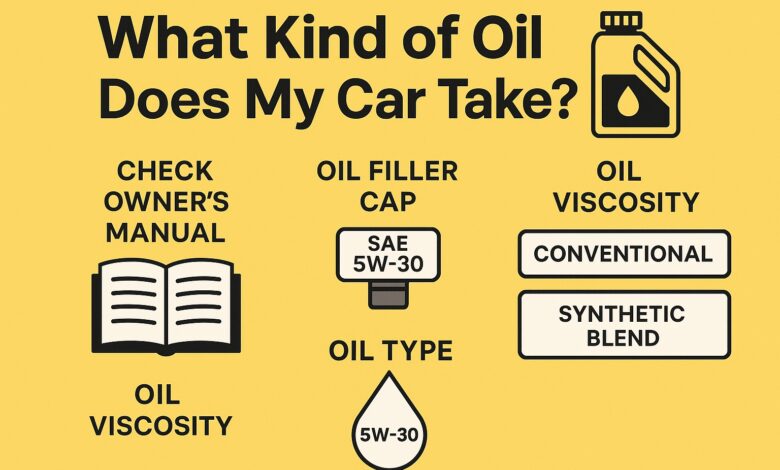
1. Consult Your Owner’s Manual
The vehicle owner manual oil recommendation is always the most reliable source. It includes the recommended engine oil type, oil change interval, and SAE oil grade like 5W-30 or 0W-20.
2. Check the Oil Filler Cap
Many modern vehicles have the recommended oil grade printed directly on the oil cap. Common grades include 5W-30 oil, 0W-20 oil, and 10W-40 oil.
3. Use an Online Car Oil Finder Tool
Brands like Castrol engine oil and Mobil engine oil offer car oil finder tools. Simply enter your car’s make, model, and year, and you’ll receive the correct oil options based on the engine oil capacity and type.
Types of Engine Oils Explained
Full Synthetic Oil
Full synthetic oil offers superior protection, improved fuel efficiency, and longer intervals between oil changes. It’s perfect for high-performance vehicles and modern engines.
Synthetic Blend (Semi-Synthetic Oil)
A semi-synthetic oil combines synthetic and conventional oils, providing better protection than conventional oil but at a lower cost than full synthetic.
Conventional Oil
Conventional oil is generally used in older vehicles with simpler engines. It’s more affordable but requires more frequent changes.
Choosing the Right Viscosity
The oil viscosity refers to how thick or thin the oil is at different temperatures. For example:
-
5W-30 oil: Ideal for general use in various climates
-
0W-20 oil: Best for cold weather and modern engines
-
10W-40 oil: Suitable for older engines or high-temperature conditions
The “W” stands for winter, and the number before and after indicates how the oil flows in cold and hot conditions respectively.
OEM Oil Specs and API Ratings
Always use oil that meets your car manufacturer’s OEM oil spec like:
-
GM Dexos approved oil
-
Ford WSS standards
-
VW/Audi 502/505
Also, check the API specifications on the bottle. For example, API SP is currently the highest gasoline engine oil standard.
Special Engine Oil Needs
High-Mileage Oil
If your car has more than 75,000 miles, high-mileage oil is designed to reduce leaks, restore seals, and enhance performance.
Best Oil for Turbo Engines
For vehicles with turbochargers, always opt for synthetic oil rated for high heat tolerance and stress resistance.
Oil for Diesel Engines
Diesel engines require oils with specific additives and formulations. Use oils labeled for diesel use to maintain performance and prevent damage.
Climate Considerations
Best Oil for Cold Weather
Choose oils with low cold temperature ratings like 0W-20 or 5W-30 for quicker engine starts and better cold start protection.
Best Oil for Hot Weather
Thicker oils like 10W-40 oil are ideal in hot environments, offering better oil performance rating at high temperatures.
Maintaining Your Engine Oil
Monitor Oil Life
Many modern cars have an oil life monitor system. Pay attention to it—it considers driving conditions, not just mileage.
Follow a Proper Oil Maintenance Schedule
Stick to your oil maintenance schedule to prevent buildup of sludge and ensure engine longevity.
Understand Oil Additives
Quality oils include oil additives like detergents, dispersants, anti-wear agents, and corrosion inhibitors for enhanced protection.
Fuel Efficiency and the Right Oil
Using the correct oil grade improves fuel efficiency. For example, thinner oils like 0W-20 reduce friction and improve mileage in many newer vehicles.
Common Questions: Answered
What Engine Oil Should I Use for My Car?
Refer to your manual or use a car oil finder tool. Ensure it meets the correct API specifications, SAE grade, and OEM oil spec.
How to Check Engine Oil Viscosity?
Look on the oil container for something like SAE 5W-30. This code describes the engine oil weight and flow characteristics.
What’s the Difference: Synthetic vs Conventional Oil?
Synthetic oil is engineered for better performance and longevity, while conventional oil is more affordable and suited to older engines.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what kind of oil your car takes is essential for maintaining engine health, improving efficiency, and avoiding costly repairs. Whether your vehicle needs synthetic oil, conventional oil, or a synthetic blend, always refer to your owner’s manual, use a trusted oil viscosity chart, and choose oil with proper API and OEM specs. Make your oil changes part of your routine maintenance, and your engine will reward you with smooth, long-lasting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I switch from conventional oil to synthetic oil?
Yes, you can switch at any time. Just make sure the synthetic oil meets your car’s specs.
Q2: What happens if I use the wrong oil?
Using the wrong oil viscosity or SAE grade can lead to poor lubrication, overheating, or engine damage.
Q3: Is high-mileage oil worth it?
For cars over 75,000 miles, high-mileage oil helps prevent leaks and reduce wear.
Q4: How often should I change my oil?
Typically every 5,000 to 7,500 miles with synthetic oil, but always check your oil maintenance schedule.
Q5: Does oil affect fuel economy?
Yes, lighter oils like 0W-20 or 5W-30 can reduce friction and improve fuel efficiency and oil performance.



